The difference between PCBA processing and assembly?
In the electronic manufacturing industry, PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) processing and assembly are two important and common concepts. Although these two terms are often mixed up, they actually involve different stages of the electronic product manufacturing process. This article will provide a detailed introduction to the differences between PCBA processing and assembly, helping enterprises better understand these two processes and optimize their production processes.
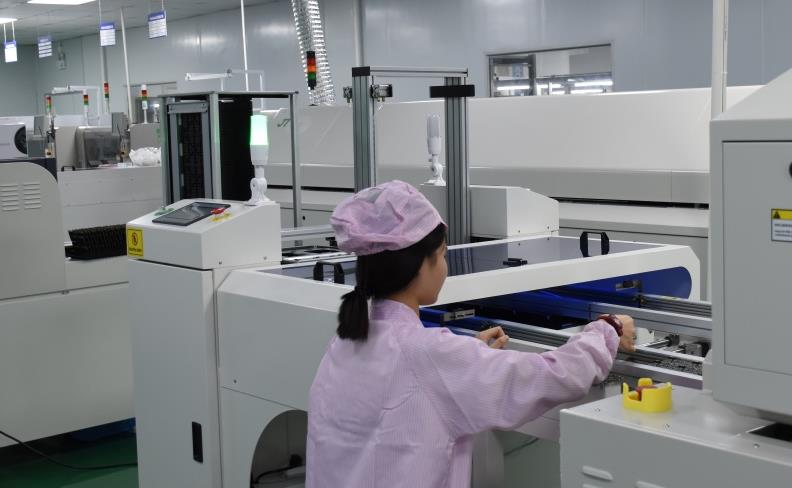
1. What is PCBA processing?
PCBA processing refers to a series of operations such as mounting, soldering, and testing components on a bare board (PCB) to make it a fully functional circuit board. This process is a core part of electronic manufacturing, as it determines whether the circuit board can function properly.
The main steps of PCBA processing
Component mounting: Use surface mount technology (SMT) or through-hole insertion technology (THT) to install components onto a PCB. SMT is suitable for small components, while THT is used for larger components.
Welding: including reflow soldering and wave soldering. Reflow soldering is used for SMT components, while wave soldering is used for THT components. The purpose of welding is to firmly fix the components on the PCB, ensuring reliable electrical connections.
Inspection: Check the welding quality and electrical performance of the circuit board through methods such as automatic optical inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection (X-Ray), and online testing (ICT) to ensure that there are no defects.
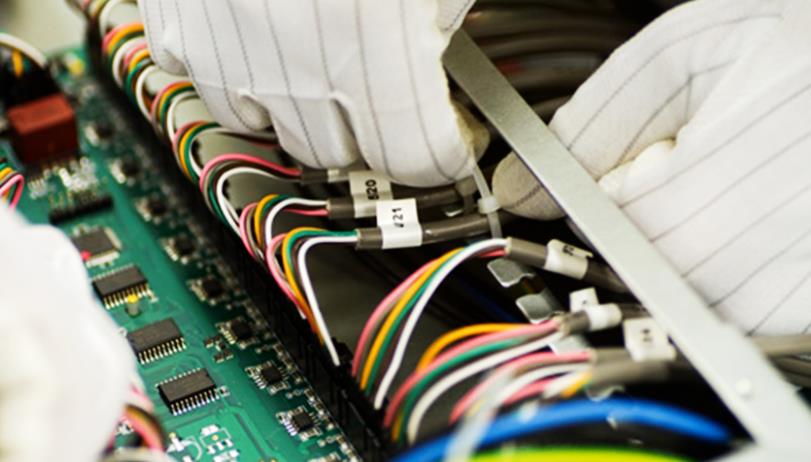

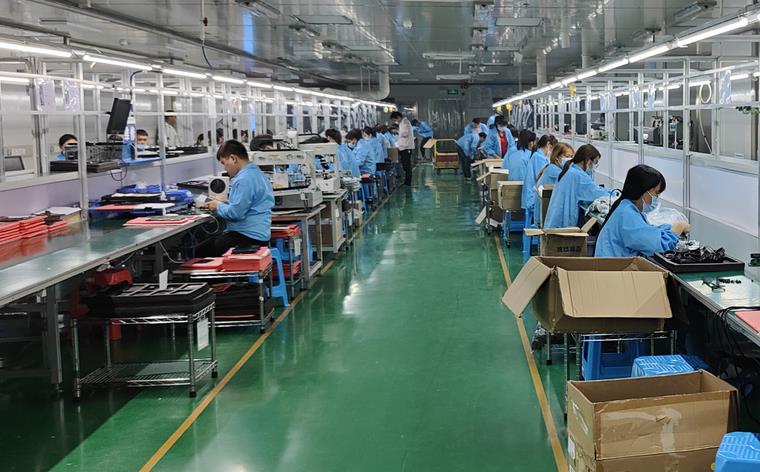
2. What is assembly?
Assembly refers to the assembly of completed PCBA processed circuit boards with other components (such as casings, connectors, heat sinks, etc.) to form a complete electronic product. Assembly is the final stage of electronic product production, which determines the final form and function of the product.
The main steps of assembly
Component assembly: Fix the PCBA onto the product casing or rack and install other necessary components such as buttons, display screens, heat sinks, etc.
Connection and testing: Connect all internal cables and interfaces, conduct a complete machine test, and ensure that all components are working properly. Including functional testing and aging testing, the former checks whether the product functions properly, while the latter verifies the long-term stability of the product.
Packaging: Clean and package products that have passed the testing, and prepare for shipment.
3. Differences between PCBA processing and assembly
Production stage
PCBA processing: Focused on the production and functional implementation of circuit boards, it is an intermediate link in the manufacturing process.
Assembly: Focusing on the assembly and functional integration of the entire product, it is the final stage of the manufacturing process.
technical requirement
PCBA processing: requires precise electronic manufacturing technology and high-precision equipment, such as SMT machines, reflow soldering machines, etc. The process requirements are extremely high to ensure the quality of welding and electrical connections.
Assembly: Proficient assembly skills and comprehensive quality control capabilities are required to ensure that each component can be installed correctly and function properly.
quality control
PCBA processing: The focus is on testing welding quality and electrical performance, using high-tech testing equipment such as AOI, X-Ray, and ICT.
Assembly: The focus is on inspecting the overall functionality and appearance quality of the machine, ensuring product reliability and user experience through functional testing and aging testing.
4. Why is it important to understand the difference between PCBA processing and assembly?
Improve production efficiency
By understanding the differences between PCBA processing and assembly, enterprises can optimize their production processes, allocate work at different stages to the most suitable team or outsource it to professional suppliers, thereby improving overall production efficiency.
Improve product quality
By conducting strict quality inspection during the PCBA processing stage, the reliability of the circuit board can be ensured, laying a solid foundation for subsequent assembly. During the assembly phase, comprehensive functional and aging testing can ensure the performance and stability of the final product.
Enhance market competitiveness
Understanding and optimizing the process of PCBA processing and assembly can enhance the technical content and market competitiveness of products. High quality products and fast delivery times will improve customer satisfaction, enhance brand image and market influence.
Although PCBA processing and assembly are important links in electronic product manufacturing, they have significant differences in production stages, technical requirements, and quality control. By gaining a deeper understanding of the differences between these two processes, enterprises can better choose different processing methods.
Tags: PCBA /PCBA_processing /PCBA_assembly /
Prev: Why is the PCB circuit board green?
Next: How to ensure quality control of PCBA processing?