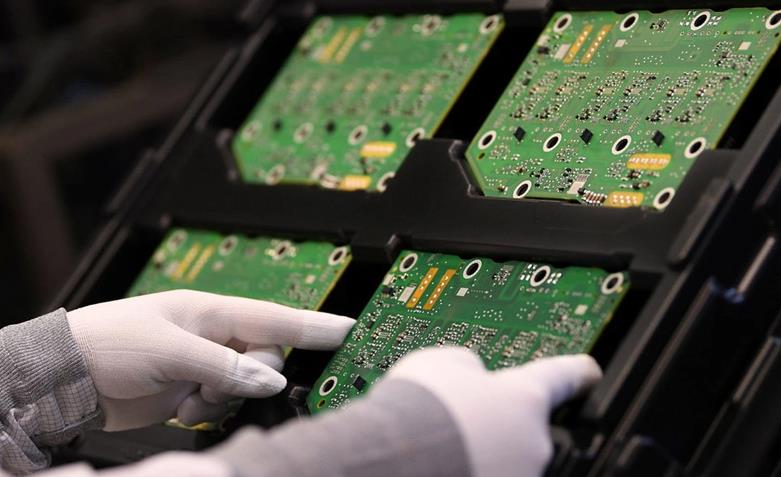
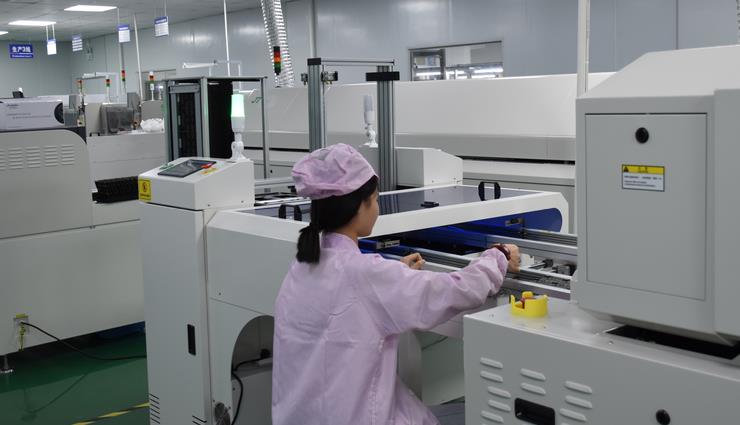
5 major PCBA processing automation production requirements
1、PCB size
Background
PCB size is limited by the capacity of electronic processing line equipment, therefore, in the product system program design should consider the appropriate PCB size.
(1) SMT equipment can be mounted on the maximum PCB size derived from the standard size of the PCB sheet, most of the 20″ × 24″, that is, 508mm × 610mm (rail width)
(2) The recommended size is the SMT production line equipment to match the size, which is conducive to the production efficiency of the equipment to eliminate equipment bottlenecks.
(3) For small-sized PCB should be designed into a collocation, in order to improve the production efficiency of the entire production line.
Design requirements
(1) In general, the maximum size of the PCB should be limited to 460mm × 610mm range.
(2) Recommended size range of (200 ~ 250) mm × (250 ~ 350) mm, aspect ratio should be <2.
(3) For size <125mm × 125mm PCB, should be collated for the appropriate size.
2、PCB shape
Background Explanation
SMT production equipment is used to transfer PCBs with guide rails, and cannot transfer PCBs with irregular profiles, especially PCBs with notched corners.
Design requirements
(1) PCB shape should be a regular square and rounded corners.
(2) In order to ensure the smoothness of the transmission process, the irregular shape of the PCB should be considered in the form of collocation will be converted into a standardized square, especially the corner of the notch is best to make up, so as to avoid wave soldering jaws in the transmission process of the cardboard.
(3) Pure SMT board, allowed to have a gap, but the gap size should be less than one-third of the length of the side where it is located, for more than this requirement, should be designed to make up the edge of the process.
(4) gold finger chamfering design in addition to the insertion side requires the design of the chamfer, the insertion of both sides of the board should also be designed (1 ~ 1.5) × 45 ° chamfer, in order to facilitate the insertion.

3、Transmission edge
Background
The size of the transfer edge depends on the equipment transfer guide requirements, printing machines, mounter and reflow soldering furnace, the general requirements of the transfer edge in 3.5mm or more.
Design requirements
(1) In order to reduce the deformation of the PCB when welding, the non-splice PCB will generally be the direction of its long side as the transmission direction; for the splice version should also be the direction of its long side as the direction of transmission.
(2) Generally, the two edges of the PCB or the transfer direction as the transfer side, the minimum width of the transfer side of 5.0mm, the transfer side of the front and back, there can not be any components or solder joints.
(3) Non-transfer edge, SMT equipment, there is no restriction, it is best to reserve 2.5mm of the components of the forbidden area.
4、Positioning holes
Background note
Plate processing, assembly, testing and many other processes require PCB accurate positioning, therefore, generally require the design of positioning holes.
Design requirements
(1) each PCB, at least two positioning holes should be designed, one designed for the round, the other designed for the long groove-shaped, the former for positioning, the latter for guidance.
Positioning hole diameter is no special requirements, according to their own factory specifications can be designed, the recommended diameter of 2.4mm, 3.0mm.
The positioning holes should be non-metalized. If the PCB is punched PCB, the positioning holes should be designed hole disk to strengthen the rigidity.
The guide hole length is generally taken as 2 times of the diameter.
Positioning hole center should be away from the transmission edge of more than 5.0mm, two positioning holes as far away as possible, it is recommended that the layout of the PCB in the diagonal.
(2) for mixed PCB (PCBA installed with plug-ins, the location of the positioning holes is best to be consistent with the front and back, so that the design of the tooling can be done on the front and back of the common, such as the installation of screws bottom bracket can also be used for plug-in trays.
5、 positioning symbols
Background
Modern placement machines, printing machines, optical inspection equipment (AOI), solder paste inspection equipment (SPI), etc. are used in the optical positioning system. Therefore, the PCB must be designed on the optical positioning symbols.
Design requirements
(1) positioning symbols are divided into the overall positioning symbols (Global Fiducial) and local positioning symbols (Local Fiducial). The former is used for the positioning of the whole board, the latter is used for collocation of sub-panel or fine-pitch components of the localization.
(2) Optical positioning symbols can be designed as a square, diamond-shaped circle, cross-shaped, tic-tac-toe, etc., the height of 2.0 mm. generally recommended that the design of Ø 1.0m round copper definition graphics, taking into account the material color and environmental contrast, leaving than the optical positioning symbols larger than the 1mm non-resistive soldering area, which does not allow any characters, the same board under the three symbols of the inner layer of the inner layer with or without copper foil should be the same.
(3) In the PCB surface with SMD components, it is recommended to lay three whole board optical positioning symbols in the corners of the board, in order to three-dimensional positioning of the PCB (three points to determine a plane, you can detect the thickness of the solder paste).
(4) For collocation, in addition to three whole board optical positioning symbols, each unit board on the diagonal is also best to design two or three collocation optical positioning symbols.
(5) For lead center distance ≤ 0.5mm QFP and center distance ≤ 0.8mm BGA and other devices, should be set in its diagonal local optical positioning symbols, in order to accurately locate it.
(6) If there are mounted components on both sides, there should be optical positioning symbols on each side.
(7) If there is no positioning holes on the PCB, the center of the optical positioning symbol should be more than 6.5mm away from the transfer side of the PCB, if there are positioning holes on the PCB, the center of the optical positioning symbol should be designed in the positioning holes against the center of the PCB side.
Tags: PCBA_processing /automation /
Prev: What is the difference between PCBA and PCB? [Chart Explanation]
Next: PCBA "three-proof" process design requirements explained