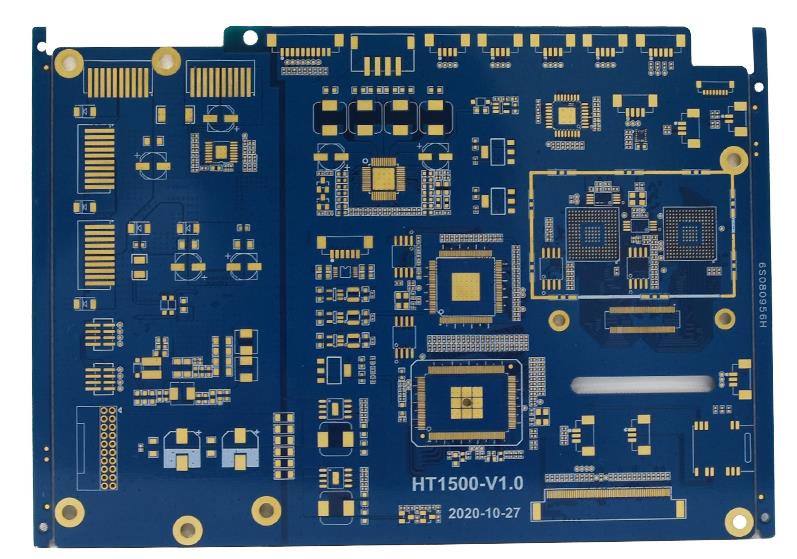
In-Depth Analysis of PCBA SMT Processes: The Core of Electronics Manufacturing
In modern electronics manufacturing, PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) and SMT (Surface Mount Technology) are essential processes. PCBA involves assembling electronic components onto a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) to create a functional board, while SMT is the leading technology that facilitates this process. With the trend of electronics moving toward miniaturization and integration, SMT technology has become crucial for manufacturers looking to enhance product quality and production efficiency.
1. Definition and Process of PCBA and SMT
PCBA refers to the process of mounting and soldering electronic components on a blank PCB, while SMT is widely used to execute this process. SMT involves placing components directly onto the PCB surface, differing from traditional through-hole technology, which requires drilling holes for component leads. SMT eliminates the need for holes, enabling a more compact PCB design.
The complete PCBA SMT process includes several steps: solder paste printing, placement, reflow soldering, cleaning, inspection, and repair. First, solder paste is printed on the PCB pads to prepare for soldering. Then, a pick-and-place machine positions surface-mount components precisely on the solder pads. Next, reflow soldering uses high temperatures to melt the solder paste, securely bonding the components to the board. The assembly then undergoes cleaning and quality inspection, with any issues identified and resolved during repair.
2. Advantages of PCBA SMT
Component Miniaturization: SMT technology enables smaller components, aligning with the trend of more compact, lightweight electronics. SMT-based PCBA products save valuable PCB space, allow for complex circuit designs, and enhance product integration.
High Production Efficiency: PCBA SMT processes support full automation. High-speed placement machines significantly reduce production time, and costs are minimized in mass production, allowing for increased output and the ability to meet large-scale demand.
Enhanced Stability: Surface-mounted components are securely fixed to the PCB, offering improved vibration resistance and temperature tolerance, making SMT ideal for high-reliability electronic devices.
3. Applications of PCBA SMT
Due to the numerous benefits of PCBA SMT, this technology is prevalent across various sectors. Consumer electronics like smartphones and tablets, which require compact sizes and stable performance, rely heavily on PCBA SMT. Additionally, industries such as industrial automation, telecommunications, medical equipment, and automotive electronics employ PCBA SMT to meet demands for high performance and reliability.


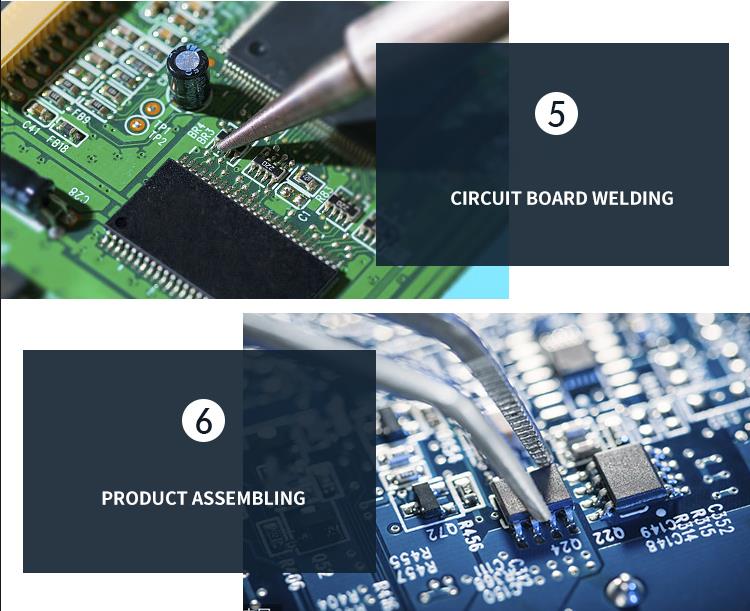
4. Future Trends in PCBA SMT
With advancing technology and changing market demands, PCBA SMT will continue evolving toward greater precision, density, and sustainability. For instance, integrating artificial intelligence in SMT processes could optimize placement speed and accuracy. More environmentally friendly solder pastes are also being used to reduce environmental impact, and 3D inspection technology allows for the detection of microscopic defects, improving product yield.
PCBA SMT plays a pivotal role in electronics manufacturing, increasing efficiency and enabling the miniaturization and integration of electronic products. For manufacturers, mastering and optimizing SMT processes is essential for enhancing product competitiveness. As PCBA SMT technology continues to progress, electronics will further evolve toward higher efficiency and sustainability, offering superior solutions for a smarter future.
Prev: 纽维实业祝愿祖国繁荣昌盛祝大家国庆快乐
Next: Shenzhou 19: Showcasing the Dual Strength of Chinese Technology and Manufacturing