What Is Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA)?
In the modern electronics manufacturing industry, Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) plays a central role. But what exactly is PCBA, and how does it impact the production of electronic devices? This article will explain the definition of PCBA, its production process, and its wide range of applications across various industries.
1. What Is Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA)?
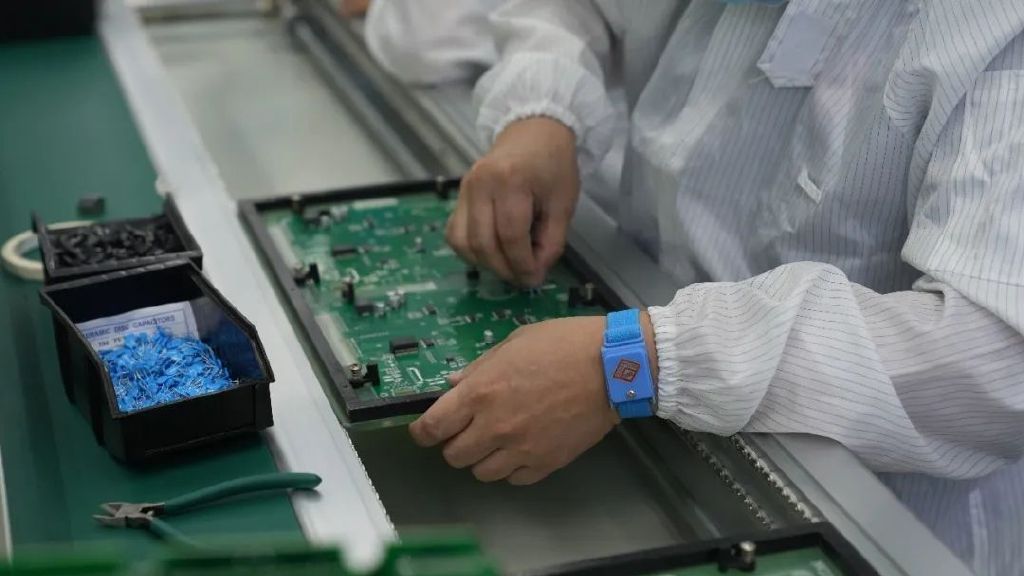
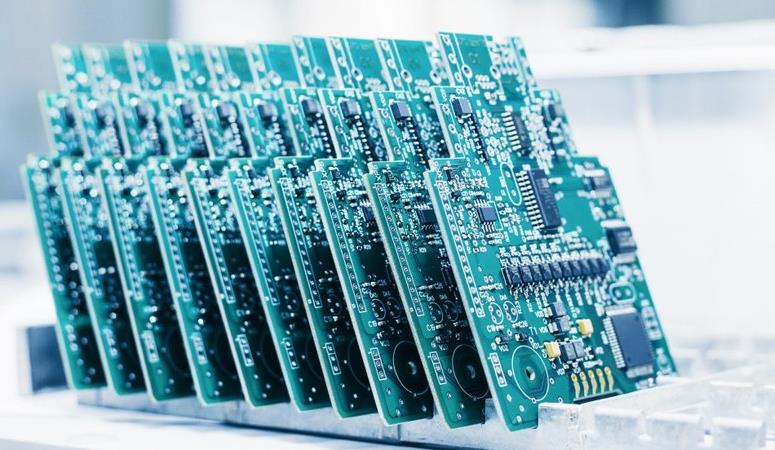
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) refers to the process of mounting electronic components onto a Printed Circuit Board (PCB), forming a complete electronic circuit.
A PCB is a board made of insulating materials like fiberglass, covered with conductive copper traces that connect various electronic components. PCBA involves assembling components such as resistors, capacitors, and microchips onto the PCB through soldering and other techniques, creating a functional electronic system.
2. The PCBA Production Process
The PCBA production process involves several precise and controlled steps to ensure the product’s performance and reliability. Here are the key steps:
1. Material Preparation and Inspection
Quality control begins with inspecting electronic components and PCBs to ensure they meet design specifications and industry standards.
2. Solder Paste Printing
Solder paste is applied to the PCB's pads using a stencil, forming the foundation for connecting components.
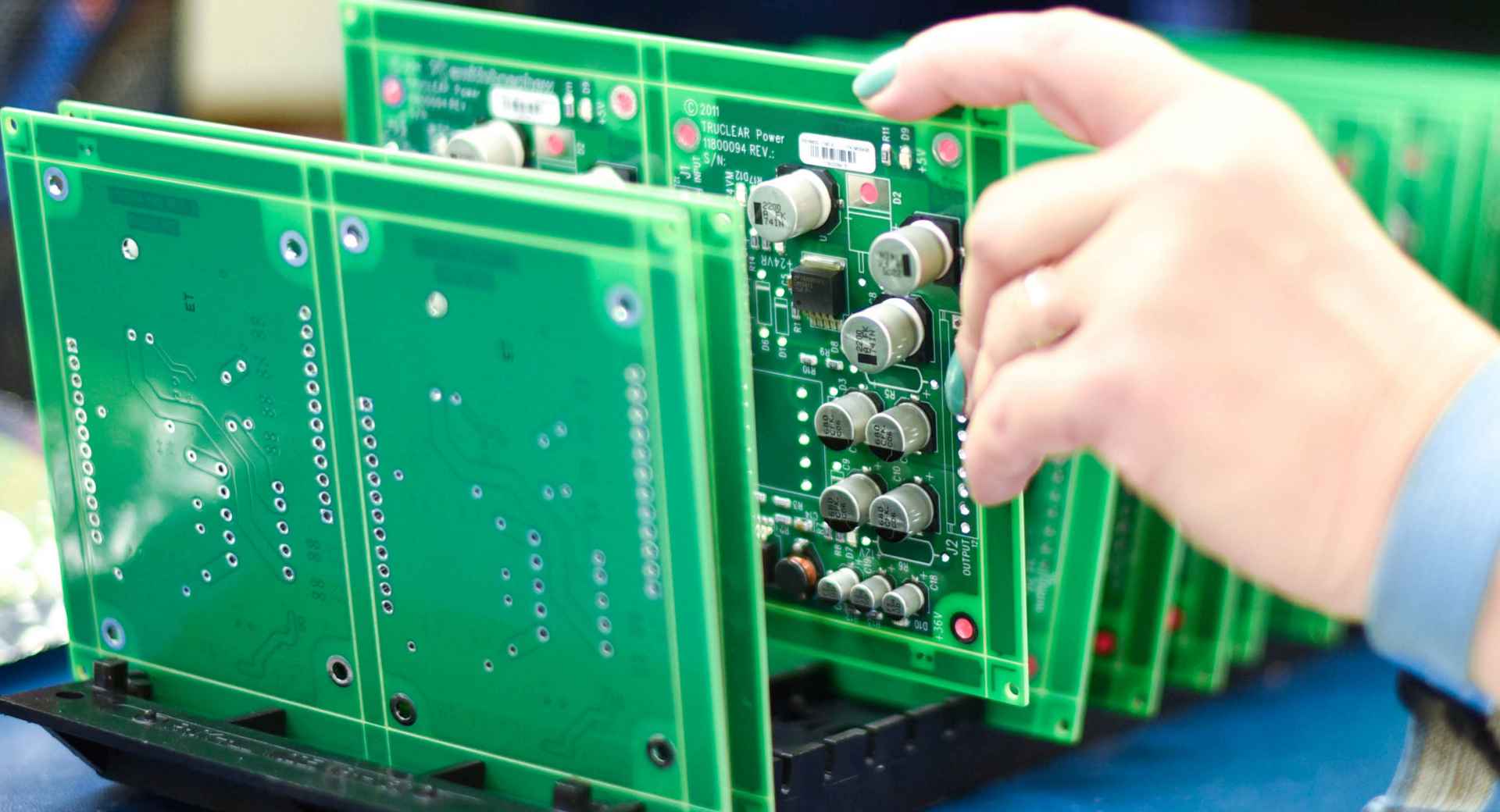
3. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly
Automated SMT machines place surface-mounted components accurately on the PCB according to the design layout.
4. Reflow Soldering
The PCB passes through a reflow oven, where heat melts the solder paste, creating secure solder joints that hold components in place.
5. Through-Hole Assembly
Large or specialized components are installed using through-hole technology, either manually or automatically.
6. Optical Inspection and Testing
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems check for soldering quality and circuit connections. Functional testing ensures the PCBA meets design and operational requirements.
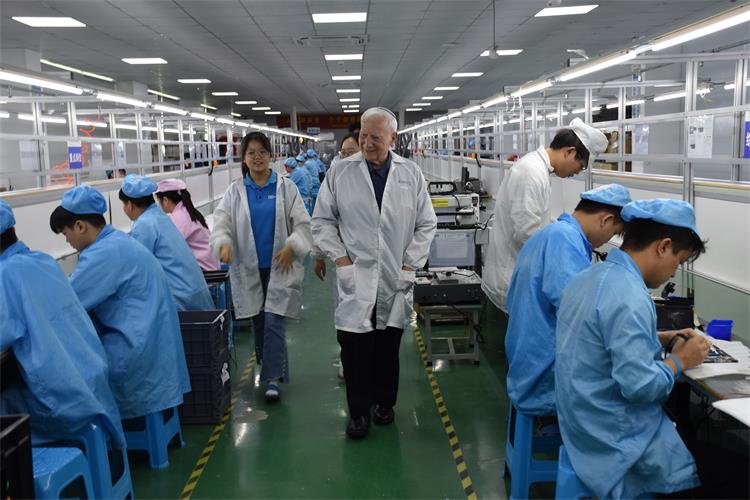

7. Assembly and Packaging
PCBA units that pass testing are assembled into final products, packaged, and prepared for shipment.
3. Applications of PCBA
PCBA is used in almost every industry that relies on electronic control. Key applications include:
1. Consumer Electronics
Smartphones, tablets, smart home devices, and more.
2. Industrial Automation
Automation equipment, industrial robots, and sensors.
3. Medical Devices
Vital sign monitors, portable medical devices, and diagnostic equipment.
4. Automotive Electronics
Car navigation systems, advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), and engine control units.
5. Communication Equipment
Wireless communication modules, routers, and satellite communication devices.
4. Why Choosing a Quality PCBA Manufacturer Matters
Selecting a reliable PCBA manufacturer is essential for ensuring product quality and competitive advantage. Consider the following factors:
- Certifications and Compliance: Look for ISO9001, CE, FCC, and other certifications.
- Manufacturing Capabilities: Check SMT assembly capacity, automated production lines, and advanced equipment.
- Quality Control and Testing: Ensure strict quality checks and comprehensive testing procedures.
- Customer Support and Delivery: Reliable customer service, technical support, and on-time delivery are critical for business success.
5. Conclusion
Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) is at the core of modern electronics manufacturing. It involves complex production steps that transform a PCB into a fully functional electronic device. Partnering with an experienced and technologically advanced PCBA manufacturer can enhance your product’s performance and market competitiveness. If you’re looking for a trusted PCBA service provider, explore industry-leading companies to discover top-quality PCBA solutions!
Tags: Printed Circuit Board Assembly /
Prev: Differences Between PWB, PCB, and PCBA
Next: What is SMT and PCBA?