What is SMT and PCBA?
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) and PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) are two essential concepts in modern electronics manufacturing, playing a crucial role in the production of smartphones, televisions, computers, automotive electronics, and many other industries. With technological advancements, the applications of SMT and PCBA have become increasingly widespread, not only improving production efficiency but also enhancing the performance and reliability of electronic products. This article will provide an in-depth understanding of these technologies, covering their definitions, working principles, and their roles in modern manufacturing.
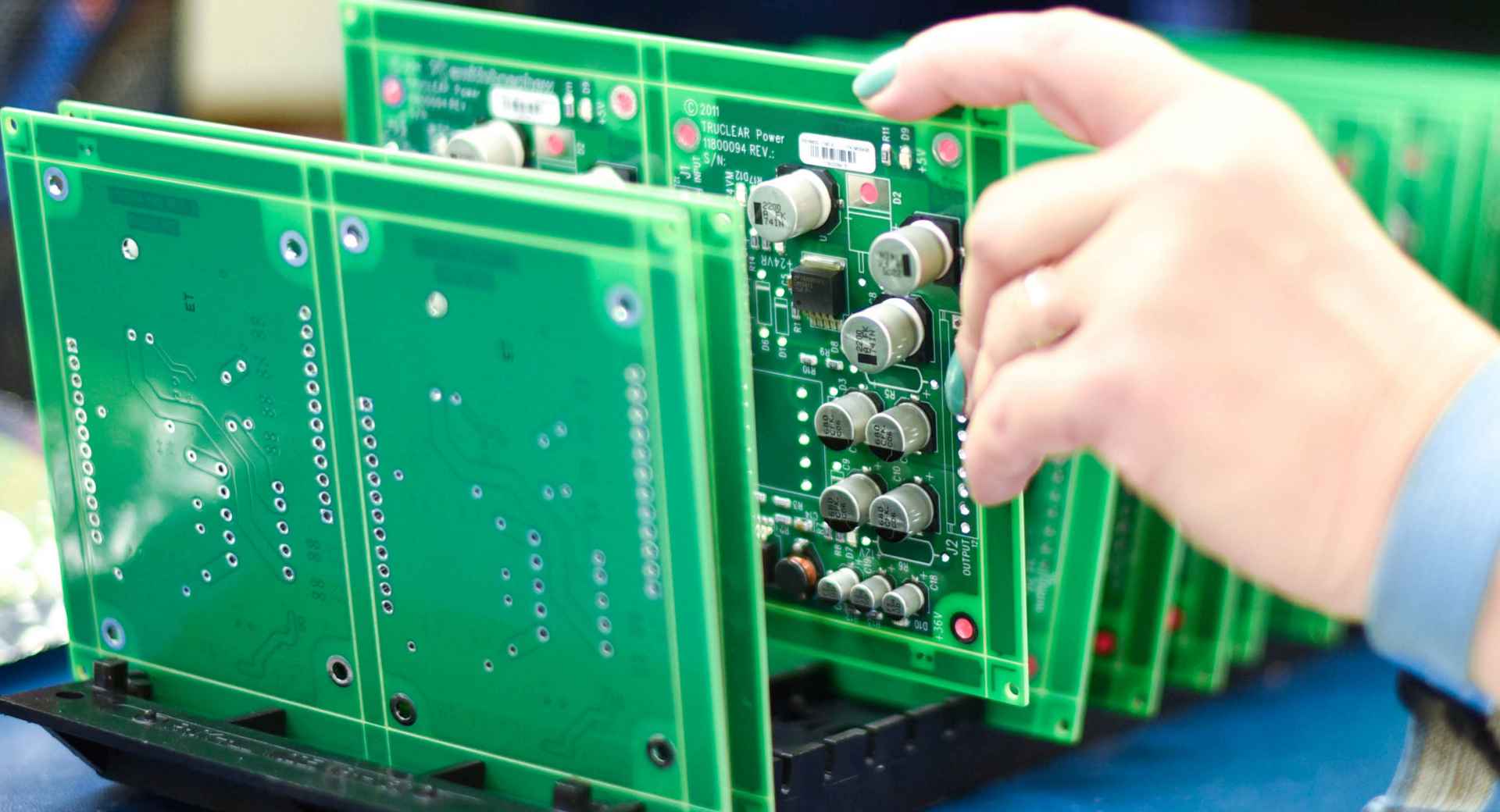
What is SMT?
SMT (Surface Mount Technology) is a manufacturing process used in electronics production, where electronic components are directly mounted onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB) rather than through-hole insertion. This allows for a higher density of components to be placed on the PCB, saving space and increasing circuit integration.
The SMT process involves several key steps: first, applying solder paste to the surface of the PCB; next, using a pick-and-place machine to accurately position electronic components onto the PCB; and finally, using a reflow soldering process to melt the solder paste, bonding the components to the board. Compared to traditional through-hole technology, SMT offers higher component density, smaller component sizes, and faster production efficiency.
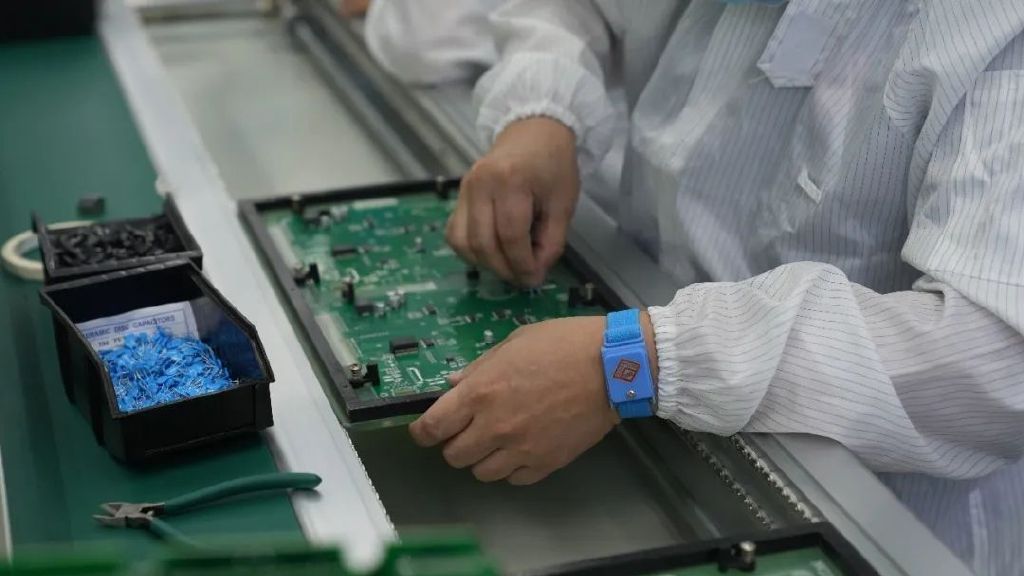

What is PCBA?
PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) refers to the process of attaching electronic components to a PCB to form a complete electronic circuit. PCBA is not just a circuit board; it is an assembled electronic system that incorporates power supply, circuit connections, and signal transmission, among other functions.
The production of a PCBA typically involves several assembly techniques, including SMT and potentially other processes like DIP (Dual In-line Package). Through these techniques, electronic components are soldered onto the PCB, creating a fully functional electronic system. The quality of PCBA directly impacts the stability and performance of the final electronic product, so quality control is crucial during production.
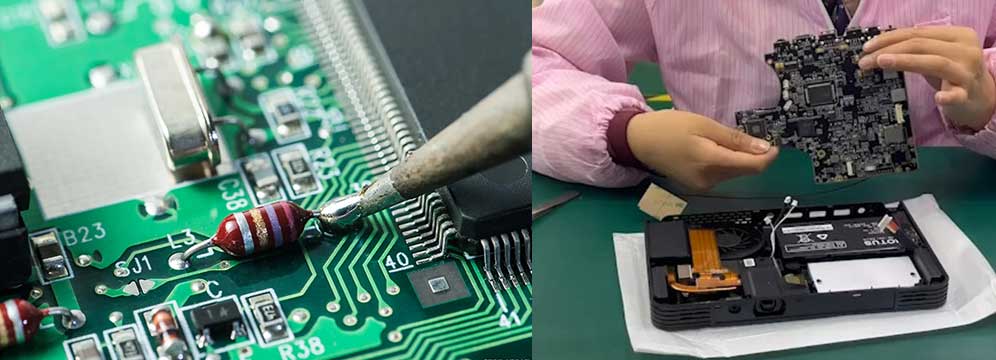
SMT and PCBA Workflow
SMT and PCBA processes are closely linked. In the PCBA production process, SMT is often the first step, setting the foundation for subsequent soldering and assembly. The typical workflow involves several steps:
- PCB Design and Manufacturing: The first step is to design the PCB based on circuit diagrams and then manufacture it.
- Solder Paste Printing: A layer of solder paste is applied to the surface of the PCB to ensure components are securely soldered to the board.
- Component Placement: A pick-and-place machine is used to position electronic components accurately onto the PCB surface.
- Reflow Soldering: The solder paste is melted using reflow soldering, ensuring the components are securely attached to the board.
- Function Testing: After assembly, the PCB is tested to ensure it functions as intended.
- DIP Soldering: For components that require through-hole mounting, a DIP soldering process is used to attach them to the PCB.
Final Inspection and Packaging: The finished PCBA is inspected for quality and then packaged for distribution.

The Importance of SMT and PCBA
In the manufacturing of electronic products, SMT and PCBA are fundamental technologies that significantly influence product performance, reliability, and cost. Here are some key contributions of SMT and PCBA to modern manufacturing:
- Improved Production Efficiency: SMT is highly automated, which significantly increases production efficiency and reduces labor costs. The automation of PCBA assembly further shortens production cycles, improving the consistency of manufacturing.
- Enhanced Product Performance: SMT enables higher integration and more compact designs, resulting in smaller, more efficient electronic products. SMT also reduces soldering defects and improves the reliability of the connections between components.
- Reduced Production Costs: By using automated production lines and precise assembly techniques, SMT and PCBA lower production costs, reduce material waste, and increase the yield of finished products.
Fostering Product Innovation: SMT allows for the integration of smaller components and higher-density circuits, which is essential for meeting the growing complexity of electronic products and driving innovation in technology.

Conclusion
As technology continues to advance, the role of SMT and PCBA in electronics manufacturing becomes even more critical. These technologies not only improve production efficiency and reduce costs but also support the high performance and miniaturization of electronic products. For businesses, mastering SMT and PCBA is key to enhancing product competitiveness and succeeding in the global marketplace. In the future, SMT and PCBA will continue to drive the development of smart devices, communication technologies, and various innovative products, leading the electronics industry into an era of more efficient and precise manufacturing.
Prev: What Is Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA)?
Next: PCB Aging Test: Ensuring Long-Term Reliability and Performance










