Wave Soldering vs. Reflow Soldering: Choosing the Right Method for Your PCB Assembly
In the electronics manufacturing industry, two common soldering techniques play a crucial role in ensuring the quality and reliability of circuit boards: wave soldering and reflow soldering. Each method has its unique advantages and is suited for specific applications. As manufacturers strive to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver high-performance products, understanding the key differences between these soldering processes can help businesses make informed decisions that best suit their needs.
What is Wave Soldering?
Wave soldering is a traditional soldering technique primarily used for through-hole components. The process involves passing the printed circuit board (PCB) over a wave of molten solder. The PCB is preheated and then conveyed over a wave of solder, which makes contact with the exposed leads of the components, creating solder joints. This method is known for its ability to handle large batches and its efficiency in assembling PCBs with through-hole components.

What is Reflow Soldering?
Reflow soldering, on the other hand, is typically used for surface-mount devices (SMDs). The process involves applying solder paste to the PCB, placing the components, and then heating the entire assembly in a reflow oven. The heat causes the solder paste to melt, forming strong, reliable solder joints between the components and the PCB. Reflow soldering is highly precise, making it ideal for small and delicate components found in modern electronics.
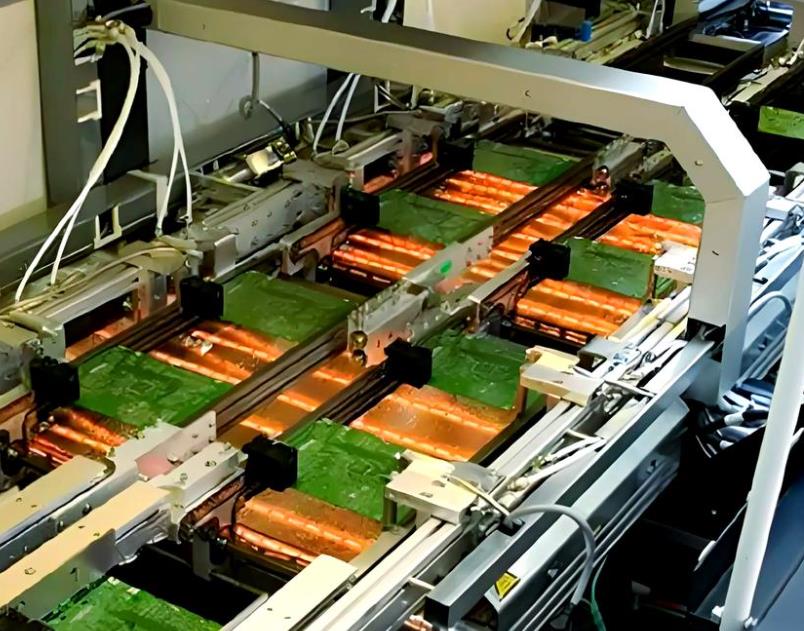

Wave Soldering vs. Reflow Soldering: Key Differences
Component Types
1.Wave Soldering is mainly used for through-hole components, where the component leads are inserted into holes on the PCB.
2.Reflow Soldering is designed for surface-mount components, which are placed directly onto the surface of the PCB without the need for holes.
Assembly Process
1.In wave soldering, the PCB is passed over a wave of molten solder, allowing the solder to flow and create connections.
2.In reflow soldering, solder paste is applied to the PCB, components are placed on top, and heat is used to melt the solder and form the connections.
Applications
1.Wave Soldering is typically used for older or more robust designs where through-hole components are still prevalent.
2.Reflow Soldering is the method of choice for most modern PCBs, especially for smaller, more compact devices that require surface-mount components.
Production Speed
1.Wave Soldering is faster for large-volume production of through-hole components.
2.Reflow Soldering is faster for surface-mount devices and is ideal for high-density PCBs.
Cost
1.Wave Soldering is often more cost-effective for low to medium production runs of through-hole designs.
2.Reflow Soldering tends to be more expensive but is essential for modern, high-precision, surface-mount designs.
Precision
1.Wave Soldering can sometimes be less precise, especially for small or sensitive components.
2.Reflow Soldering offers higher precision, especially for small, fine-pitch components.

Choosing the Right Soldering Method
Choosing between wave soldering and reflow soldering depends on the specific needs of your PCB assembly. For older designs with through-hole components, wave soldering remains an efficient and cost-effective solution. On the other hand, for modern designs with high-density surface-mount components, reflow soldering offers superior precision and performance.
By understanding the strengths of each soldering technique, businesses can optimize their production processes, reduce costs, and ensure the reliability of their products.
Tags: PCBA /PCB Assembly /Wave Soldering /Reflow Soldering /
Prev: SMD vs SMT: Understanding the Key Differences in Electronics Assembly
Next: How to Choose the Right PCBA Supplier? Key Factors Explained